The nursing shortage in the United States has reached a critical juncture, posing significant challenges to the healthcare system. While various factors contribute to this crisis, the repercussions of the shortage are most acutely felt in patient care. Understanding the nexus between nursing scarcity and patient outcomes is essential for policymakers, healthcare administrators, and the public at large.
The multi-faceted factor effects of nursing shortage
Hospital acuity
As the demand for hospital care rises- a more skilled nursing jobs workforce. Advances in medical technology and changes in patient care models have escalated hospital acuity levels.
The result? A higher demand for specialized nursing skills and competencies exacerbates the effects of nursing shortage.
Aging population and workforce
The aging Baby Boomer population presents a double-edged sword. As this demographic requires more healthcare services, the nursing workforce—55% of whom are 50 years or older—faces an aging crisis.
A confluence of retirements and increased demand strains the system, further compromising patient care because of the effects of nursing shortage.
Workload and environment
Cost containment measures in healthcare have led to staffing reductions and mandatory overtime policies. While these strategies aim to manage expenses, they create a high-stress environment for nurses.
Heavy workloads and unfavorable working conditions discourage both entry into and retention within the nursing job profession, perpetuating the effects of nursing shortage and compromising patient care quality.
Implications for patient care
- Decreased quality of care: Overworked nurses may experience burnout, leading to increased medical errors, compromised patient safety, and suboptimal outcomes.
- Reduced access: The nursing shortage limits healthcare access, particularly in underserved areas, exacerbating health disparities and leaving vulnerable populations at risk.
- Economic impact: The nursing shortage drives up healthcare costs as hospitals grapple with staffing challenges, leading to inefficiencies and increased patient lengths of stay.
Strategies for mitigating the nursing shortage
Strengthening nursing job education
- Faculty recruitment and retention
Competitive compensation packages, professional development opportunities, and mentorship programs can attract and retain qualified nursing faculty.
Additionally, innovative teaching models, such as online education and simulation-based learning, can alleviate the strain on clinical placements.
- Expand educational capacity
Collaboration between nursing jobs, schools, healthcare institutions, and policymakers can facilitate the expansion of nursing programs, including the establishment of new schools and satellite campuses in underserved areas.
Enhancing workforce development
- Addressing workforce retention
Implementing evidence-based staffing models, reducing mandatory overtime, and fostering supportive work environments can improve nurse retention rates.
Furthermore, investing in continuing education and career advancement opportunities can incentivize nurses to remain in the profession.
- Diversifying the nursing pipeline
Promoting diversity and inclusion in nursing education and practice can help address workforce shortages while addressing health disparities.
Scholarships, loan forgiveness programs, and outreach initiatives targeting underrepresented groups can broaden the nursing talent pool.
Leveraging technology and innovation
- Telehealth and remote monitoring
Leveraging technology, such as telehealth and remote monitoring tools, can expand access to care and alleviate the burden on nursing staff.
By facilitating virtual consultations and remote patient monitoring, nurses can provide timely interventions without geographical constraints.
- Interprofessional collaboration
Encouraging collaboration between nurses, physicians, pharmacists, and other healthcare professionals can enhance care coordination and optimize resource utilization.
Interprofessional education and team-based care models can foster mutual respect, communication, and collaboration among healthcare providers.
Policy and advocacy
- Legislative support
Policymakers must prioritize funding for nursing jobs, education, research, and workforce development initiatives.
After advocating for policies that address licensure requirements, scope of practice regulations, and reimbursement models, policymakers can create an enabling environment for nursing practice and education.
- Public awareness and engagement
Raising public awareness about the importance of nursing and its impact on patient care can garner support for workforce development initiatives.
Engaging with community stakeholders, advocacy groups, and healthcare organizations can build momentum for addressing the nursing shortage on a national scale.
Benefits of becoming a nurse
Nursing is a rewarding career that offers many benefits. Here are six of the top reasons to become a nurse:
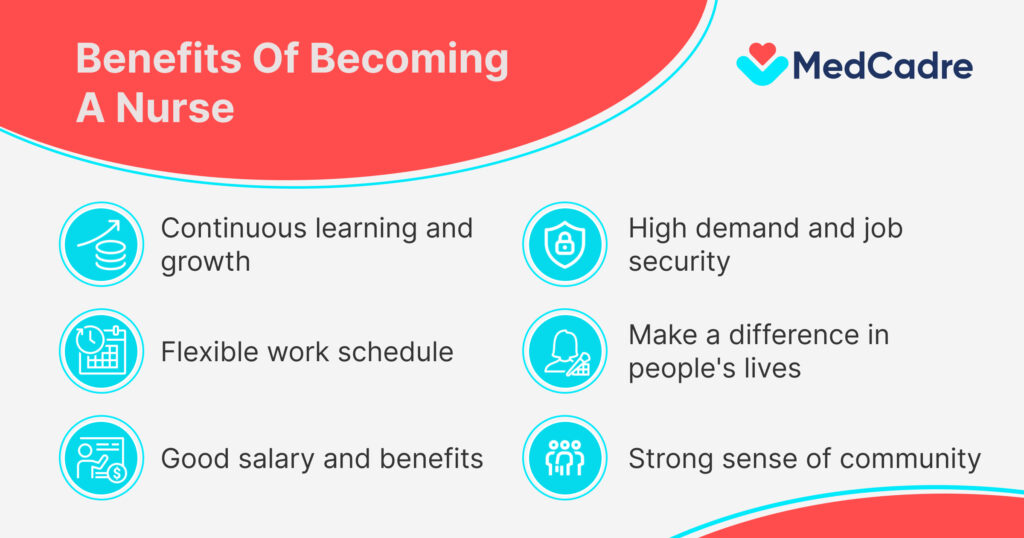
- Make a difference in people’s lives: As a nurse, you will have the opportunity to care for people at their most vulnerable times. You will play a vital role in their recovery and healing, and you will make a real difference in their lives.
- High demand and job security: The nursing profession is in high demand worldwide, and this is expected to continue for many years to come. This means that you are guaranteed to have a job after you graduate from nursing school.
- Good salary and benefits: Nurses earn a good salary and benefits package. The average annual salary for a registered nurse in the United States is $80,010.
- Flexible work schedule: Nurses have a variety of work schedule options to choose from. You can work full-time, part-time, or per diem. You can also work days, nights, or weekends. This flexibility is great for people who want to balance their work life with their personal life.
- Continuous learning and growth: Nursing is a field that is constantly changing. There are always new technologies and treatments to learn about. This means that you will never get bored in your job.
- Strong sense of community: Nurses are a close-knit community. They support each other and work together as a team. This can be a great source of strength and support.
Read more – Travel Nurse Salaries In 2024: What To Expect
Nursing opportunities in the future
New opportunities for nursing professionals are emerging. The future promises exciting possibilities for those entering or already in the nursing field:
- Technological integration: Nurses will play a crucial role in harnessing technology, including artificial intelligence and telehealth, to enhance patient care and streamline healthcare delivery.
- Specialized roles: Increasing demand for specialized care will create opportunities for nurses to specialize in areas such as geriatrics, mental health, and critical care.
- Leadership and advocacy: Nurses will have the chance to take on leadership roles and advocate for policy changes that promote patient well-being.
- Global health opportunities: The interconnected world offers opportunities for nurses to engage in global health initiatives, contributing their skills to address healthcare challenges on a global scale.
- Innovation in education: The need for nurse educators will drive innovation in nursing education, with the development of new teaching methodologies and online learning platforms.
- Community and public health: Nurses will continue to play a vital role in promoting community and public health, and addressing preventive care and health disparities.
- Collaborative care models: Inter professional collaboration will become increasingly important, creating opportunities for nurses to work closely with other healthcare professionals for holistic patient care.
- Research and evidence-based practice: The emphasis on evidence-based practice will lead to increased opportunities for nurses to engage in research, contributing to advancements in healthcare knowledge and practices.
Conclusion
The U.S. nursing shortage highlights challenges in patient care and workforce sustainability, driven by factors like faculty shortages and aging demographics.
Collaboration among policymakers, educators, and healthcare administrators is crucial to address this crisis.
Investing in education, retention strategies, and technology can help build a resilient nursing workforce.
Future opportunities in areas like technology integration, specialized roles, and global health offer avenues for nurses to adapt and excel.
For those seeking nursing jobs in the USA, MedCadre will help you to get into the healthcare industry, you just need to check the MedCadre career page we have a list of opportunities, else drop us your CV, and our recruitment team will analyze your profile thoroughly and give you a call with the suitable job as per your skills and experience.
Prioritizing nursing workforce development is essential for quality patient care, health equity, and a sustainable healthcare future.






